Introduction to PCB 3D Design
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design has evolved significantly over the years, and one of the most notable advancements is the incorporation of 3D functions. PCB 3D design has revolutionized the way engineers and designers approach circuit board development, enabling them to create more efficient, compact, and reliable products. In this article, we will explore the reasons why PCB design uses 3D functions and how they benefit the electronics industry.
The Need for 3D Visualization in PCB Design
Traditional PCB design relied on 2D schematics and layouts, which provided a flat representation of the circuit board. However, as electronic devices became more complex and compact, designers faced challenges in visualizing the spatial relationships between components, traces, and layers. This is where 3D visualization comes into play.
By using 3D functions in PCB design software, engineers can:
- Visualize the PCB from various angles and perspectives
- Identify potential issues related to component placement and clearance
- Optimize the use of available space within the device enclosure
- Enhance collaboration between design teams and stakeholders
Benefits of PCB 3D Design
Incorporating 3D functions in PCB design offers several key benefits:
-
Improved Design Accuracy: 3D visualization allows designers to identify and resolve issues related to component placement, trace routing, and layer stackup early in the design process. This reduces the likelihood of errors and the need for costly revisions later on.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: 3D models of PCBs can be easily shared among design teams, manufacturers, and stakeholders. This facilitates better communication and collaboration, ensuring that everyone involved in the project has a clear understanding of the design intent and requirements.
-
Faster Time-to-Market: By catching and resolving design issues early, 3D PCB design helps to streamline the development process. This leads to faster prototyping, testing, and ultimately, a quicker time-to-market for the final product.
-
Cost Savings: Identifying and addressing design issues early in the development cycle helps to minimize the need for physical prototypes and iterations. This translates to significant cost savings in terms of materials, labor, and time.
3D Functions in PCB Design Software
Modern PCB design software packages offer a range of 3D functions to assist engineers in creating accurate and efficient designs. Some of the most common 3D functions include:
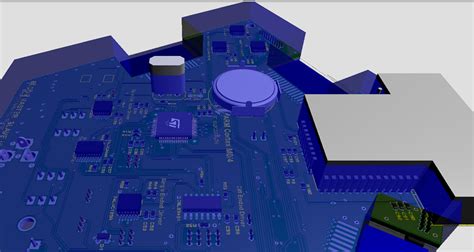
3D Modeling and Visualization
PCB design software allows users to create detailed 3D models of their circuit boards, including components, traces, and mechanical features. These models can be viewed from various angles and zoomed in or out for closer inspection. Designers can also apply realistic textures and colors to the components and board surfaces for a more accurate representation.
Collision Detection and Clearance Checking
3D PCB design tools offer collision detection and clearance checking functions to ensure that components and traces do not interfere with each other or with mechanical features of the device enclosure. These functions automatically highlight potential issues, such as component overlaps or insufficient clearances, allowing designers to make necessary adjustments.
3D Measurements and Analysis
With 3D PCB design, engineers can easily measure distances, angles, and volumes within the circuit board assembly. This is particularly useful for ensuring proper fit and clearance within the device enclosure. Additionally, some software packages offer thermal analysis capabilities, allowing designers to simulate and optimize the thermal performance of the PCB in a 3D environment.
3D Data Export and Collaboration
Most PCB design software supports the export of 3D models in various file formats, such as STEP, IGES, or OBJ. These files can be shared with mechanical design teams, manufacturers, or other stakeholders for further analysis, collaboration, or integration into the overall device assembly. Some software packages also offer built-in collaboration tools, allowing team members to work on the same 3D PCB design simultaneously.
Real-World Applications of PCB 3D Design
PCB 3D design has found widespread adoption across various industries, from consumer electronics to aerospace and defense. Some notable applications include:
-
Smartphones and Wearables: The compact and densely packed nature of modern smartphones and wearables necessitates the use of 3D PCB design to optimize component placement and minimize device size.
-
Automotive Electronics: As vehicles incorporate more advanced electronic systems, such as driver assistance features and infotainment, 3D PCB design helps to create reliable and space-efficient electronic modules.
-
Medical Devices: PCB 3D design is crucial in the development of compact and reliable medical devices, such as implantable sensors and wearable monitoring systems.
-
Aerospace and Defense: In the aerospace and defense industries, where reliability and performance are paramount, 3D PCB design ensures that electronic systems can withstand harsh environments and meet stringent requirements.

The Future of PCB 3D Design
As electronic devices continue to become more complex and compact, the importance of 3D functions in PCB design will only grow. Some of the trends and developments we can expect to see in the future include:
-
Integration with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies will enable designers to interact with 3D PCB models in immersive environments, facilitating better visualization and collaboration.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms will be integrated into PCB design software to automate and optimize various aspects of the design process, such as component placement, trace routing, and thermal analysis.
-
Advancements in 3D Printing: As 3D printing technologies evolve, we may see the emergence of fully 3D-printed PCBs, which could revolutionize the way electronic devices are manufactured and assembled.
FAQs
-
Q: What is PCB 3D design?
A: PCB 3D design refers to the use of three-dimensional modeling and visualization functions in printed circuit board design software. It allows engineers to create accurate and detailed representations of PCBs, including components, traces, and mechanical features. -
Q: Why is 3D PCB design important?
A: 3D PCB design is important because it helps engineers to create more accurate, efficient, and reliable circuit boards. By visualizing the PCB in 3D, designers can identify and resolve issues related to component placement, trace routing, and clearances early in the design process, reducing the need for costly revisions and improving overall product quality. -
Q: What are some common 3D functions in PCB design software?
A: Some common 3D functions in PCB design software include 3D modeling and visualization, collision detection and clearance checking, 3D measurements and analysis, and 3D data export and collaboration. -
Q: What industries benefit from PCB 3D design?
A: PCB 3D design is used across various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and defense. It is particularly beneficial for applications that require compact, high-performance, and reliable electronic systems. -
Q: What future developments can we expect in PCB 3D design?
A: The future of PCB 3D design may involve integration with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies, the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms for design optimization, and advancements in 3D printing for fully 3D-printed PCBs.
Conclusion
PCB 3D design has become an essential tool for engineers and designers in the electronics industry. By incorporating 3D functions into the design process, professionals can create more accurate, efficient, and reliable circuit boards while reducing development time and costs. As electronic devices continue to evolve and become more complex, the use of 3D PCB design will only become more prevalent, driving innovation and shaping the future of the industry.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Design Accuracy | Identify and resolve issues related to component placement, trace routing, and layer stackup |
| Enhanced Collaboration | Facilitate communication and understanding among design teams, manufacturers, and stakeholders |
| Faster Time-to-Market | Streamline the development process by catching and resolving design issues early |
| Cost Savings | Minimize the need for physical prototypes and iterations, saving materials, labor, and time |
Table 1: Benefits of PCB 3D Design
By embracing 3D functions in PCB design, engineers and designers can unlock new possibilities in the development of electronic devices, leading to more innovative, reliable, and cost-effective products that meet the ever-increasing demands of the modern world.
No responses yet