Understanding the Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant, also known as relative permittivity (εr), is a measure of a material’s ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is the ratio of the permittivity of a material to the permittivity of free space. The dielectric constant is a dimensionless quantity and is always greater than or equal to 1.
Factors Affecting the Dielectric Constant
Several factors can influence the dielectric constant of a material, including:
-
Frequency: The dielectric constant of a material can vary with the frequency of the applied electric field. At higher frequencies, the dielectric constant tends to decrease.
-
Temperature: The dielectric constant of a material can also change with temperature. In general, the dielectric constant increases with increasing temperature.
-
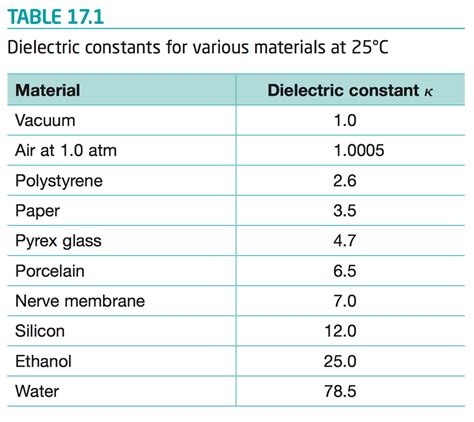
Moisture content: The presence of moisture in a material can significantly affect its dielectric constant. Water has a high dielectric constant (approximately 80), so even small amounts of moisture can increase the overall dielectric constant of a material.
-
Material composition: The chemical composition and structure of a material play a significant role in determining its dielectric constant. Materials with polar molecules tend to have higher dielectric constants than those with non-polar molecules.
High TG FR4 and its Dielectric Constant
High TG FR4 is a composite material consisting of a woven fiberglass fabric impregnated with an epoxy resin. The glass transition temperature (Tg) of High TG FR4 is higher than that of standard FR4, typically ranging from 170°C to 180°C. This higher Tg allows High TG FR4 to maintain its mechanical and electrical properties at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for applications that require higher thermal stability.
Typical Dielectric Constant Values for High TG FR4
The dielectric constant of High TG FR4 can vary depending on the specific formulation and manufacturing process. However, typical values for the dielectric constant of High TG FR4 at various frequencies are as follows:
| Frequency | Dielectric Constant (εr) |
|---|---|
| 1 MHz | 4.5 – 4.7 |
| 10 MHz | 4.4 – 4.6 |
| 100 MHz | 4.3 – 4.5 |
| 1 GHz | 4.2 – 4.4 |
It is important to note that these values are approximate and can vary depending on the specific manufacturer and grade of High TG FR4.
Comparison with Standard FR4
Standard FR4 has a glass transition temperature of around 130°C to 140°C, which is lower than that of High TG FR4. The dielectric constant of standard FR4 is similar to that of High TG FR4, with typical values ranging from 4.2 to 4.6 at various frequencies.
However, the higher glass transition temperature of High TG FR4 allows it to maintain its dielectric constant and other properties at higher temperatures, making it a better choice for applications that require higher thermal stability.
Applications of High TG FR4
High TG FR4 is used in a wide range of applications that require high thermal stability and good electrical properties. Some of the most common applications include:
-
Automotive electronics: High TG FR4 is used in automotive electronic systems, such as engine control units (ECUs), power electronics, and sensors, where high temperature resistance is crucial.
-
Aerospace and defense: The aerospace and defense industries use High TG FR4 for various applications, such as avionics, radar systems, and satellite communications, due to its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
-
Industrial electronics: High TG FR4 is used in industrial electronic systems, such as motor drives, power supplies, and automation equipment, where high reliability and thermal stability are essential.
-
Telecommunications: High TG FR4 is used in telecommunications equipment, such as base stations, routers, and switches, where high-frequency performance and thermal stability are critical.
-
Medical devices: The medical industry uses High TG FR4 for various applications, such as implantable devices, diagnostic equipment, and surgical instruments, due to its biocompatibility and high reliability.

Designing with High TG FR4
When designing PCBs using High TG FR4, it is essential to consider the material’s dielectric constant and other properties to ensure optimal performance. Some key considerations include:
-
Impedance control: The dielectric constant of High TG FR4 affects the characteristic impedance of transmission lines on the PCB. Designers must carefully calculate and control the impedance to ensure proper signal integrity and minimize reflections.
-
Layer stackup: The layer stackup of a High TG FR4 PCB should be designed to minimize signal distortion and crosstalk. This may involve using ground planes, power planes, and appropriate spacing between layers.
-
Via design: Vias are used to connect different layers of a PCB. When designing with High TG FR4, it is essential to consider the via size, placement, and spacing to minimize signal distortion and ensure reliable connections.
-
Thermal management: Although High TG FR4 has better thermal stability than standard FR4, it is still important to consider thermal management in the PCB design. This may involve using thermal vias, heat sinks, or other cooling techniques to dissipate heat effectively.
-
Manufacturing considerations: High TG FR4 may require specific manufacturing processes and parameters to ensure optimal performance. Designers should work closely with their PCB manufacturer to ensure that the design can be manufactured reliably and cost-effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the main difference between High TG FR4 and standard FR4?
The main difference between High TG FR4 and standard FR4 is the glass transition temperature (Tg). High TG FR4 has a higher Tg (170°C to 180°C) compared to standard FR4 (130°C to 140°C), which allows it to maintain its mechanical and electrical properties at higher temperatures. -
Does the dielectric constant of High TG FR4 change with frequency?
Yes, the dielectric constant of High TG FR4 can vary with frequency. In general, the dielectric constant tends to decrease slightly as the frequency increases. -
Can moisture affect the dielectric constant of High TG FR4?
Yes, moisture can significantly affect the dielectric constant of High TG FR4. Even small amounts of moisture can increase the overall dielectric constant of the material, as water has a high dielectric constant (approximately 80). -
What are some common applications of High TG FR4?
High TG FR4 is commonly used in applications that require high thermal stability and good electrical properties, such as automotive electronics, aerospace and defense systems, industrial electronics, telecommunications equipment, and medical devices. -
What are some key considerations when designing PCBs with High TG FR4?
When designing PCBs with High TG FR4, it is essential to consider factors such as impedance control, layer stackup, via design, thermal management, and manufacturing considerations to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
In conclusion, understanding the dielectric constant of High TG FR4 is crucial for designers and engineers working with this material in various applications. By considering the factors that affect the dielectric constant and the key design considerations, they can create PCBs that offer high performance, reliability, and thermal stability. As technology continues to advance, the demand for materials like High TG FR4 that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and maintain their properties at elevated temperatures will only continue to grow.
No responses yet