Introduction to TL07x Operational Amplifiers
The TL07x series of operational amplifiers, which includes the TL071, TL072, and TL074, are widely used in various analog circuit applications. These op-amps are known for their low noise, high slew rate, and wide bandwidth, making them suitable for a range of tasks such as signal conditioning, filtering, and amplification. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, applications, and circuit designs involving the TL07x op-amps.
Key Features of TL07x Op-Amps
| Feature | TL071 | TL072 | TL074 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Op-Amps | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Input Offset Voltage | 3 mV (max) | 3 mV (max) | 3 mV (max) |
| Input Bias Current | 65 pA (max) | 65 pA (max) | 65 pA (max) |
| Slew Rate | 13 V/μs | 13 V/μs | 13 V/μs |
| Gain-Bandwidth Product | 3 MHz | 3 MHz | 3 MHz |
| Supply Voltage Range | ±5 V to ±18 V | ±5 V to ±18 V | ±5 V to ±18 V |
The TL07x op-amps offer excellent performance characteristics, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. The low input offset voltage and input bias current ensure accurate signal processing, while the high slew rate and gain-bandwidth product allow for fast and precise amplification of signals.
Basic TL07x Circuit Configurations
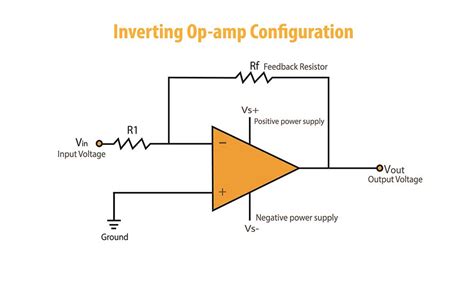
Inverting Amplifier
The inverting amplifier is a common configuration used with TL07x op-amps. It provides an output signal that is inverted and amplified with respect to the input signal. The gain of the inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (R2) to the input resistor (R1).
+Vcc
|
|
+-+
| \
| \
| \
| |
R2 | |
| |
| /
| /
| /
+-+
|
| TL07x
+--+--+ +-----+-----+
| | | | |
| +------|+ | |
| R1 | | |
| |- | |
| +------| +-----+
+--+--+ | |
| | |
| +-----+-----+
| |
-|- -|-
Vin | | Vout
| |
GND GND
The gain of the inverting amplifier is given by:
Gain = -R2 / R1
Non-Inverting Amplifier
The non-inverting amplifier configuration provides an output signal that is in phase with the input signal and amplified. The gain of the non-inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (R2) to the input resistor (R1), plus one.
+Vcc
|
|
+-+
| \
| \
| \
| |
R2 | |
| |
| /
| /
| /
+-+
|
|
+-+
| \
| \
| \
| |
R1 | | TL07x
| | +-----+-----+
| / | | |
| / |+ | |
| / | | |
+-+ |- | |
| | +-----+
| | |
+-------| |
+-----+-----+
|
-|-
| Vout
|
GND
The gain of the non-inverting amplifier is given by:
Gain = 1 + (R2 / R1)
Voltage Follower (Buffer)
The voltage follower, also known as a buffer, is a special case of the non-inverting amplifier where the feedback resistor (R2) is replaced with a short circuit. This configuration provides a unity gain (gain = 1) and is used to isolate a high-impedance source from a low-impedance load, preventing loading effects.
TL07x
+-----+-----+
| | |
|+ | |
| | |
|- | |
| +-----+
| |
+-----+-----+
|
-|-
| Vout
|
GND
The voltage follower has a gain of 1, meaning the output voltage is equal to the input voltage:
Vout = Vin
Advanced TL07x Circuit Applications
Active Filters
TL07x op-amps can be used to implement various types of active filters, such as low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters. These filters are used to selectively attenuate or pass certain frequencies while rejecting others. The filter characteristics, such as cut-off frequency and order, can be controlled by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the circuit.
Example: Second-Order Low-Pass Filter (Sallen-Key Topology)
+Vcc
|
|
R1 |
+---/\/\-+
| |
-|- +-+
| C1 | \ TL07x
+---||--+ \ +-----+-----+
| | | | |
+----+--|+ | |
| | | |
+--| | |
| | +-----+
+--| |
| | |
| +-----+-----+
| |
| -|-
| | Vout
| |
GND GND
The cut-off frequency (fc) of the second-order low-pass filter is given by:
fc = 1 / (2π√(R1^2 * C1 * C2))
Instrumentation Amplifiers
Instrumentation amplifiers are used to amplify small differential signals while rejecting common-mode noise. They are commonly used in measurement and data acquisition systems. TL07x op-amps can be used to build instrumentation amplifiers by combining multiple op-amp stages.
Example: Three Op-Amp Instrumentation Amplifier
+Vcc
|
|
+-+
| \
| \
| \ TL072
| +---+-----+-----+
| | | | |
| / |+ | |
| / | | |
| / |- | |
+-+ | +-----+
| | |
+-----/\/\-----+--------+ |
| R1 | |
| | +-----+-----+
-|- | | | |
| Vin+ | R3 |+ | |
+-----/\/\-----+---/\/\-| | |
| R2 | |- | |
| | | +-----+
+-----/\/\-----+ | |
| R1 | | |
-|- | +-----+-----+
| Vin- | |
| | -|-
| | | Vout
| | |
GND GND GND
The gain of the three op-amp instrumentation amplifier is given by:
Gain = (1 + 2R1 / R2) * (R3 / R1)

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between TL071, TL072, and TL074 op-amps?
A: The main difference between these op-amps is the number of op-amp circuits included in each package. TL071 contains a single op-amp, TL072 contains two op-amps, and TL074 contains four op-amps. The electrical characteristics and performance of the individual op-amps are the same across the TL07x series. -
Q: Can TL07x op-amps be used with single-supply operation?
A: Yes, TL07x op-amps can be used with single-supply operation, typically ranging from 5 V to 18 V. However, it’s important to ensure that the input and output voltages remain within the supply voltage range to avoid clipping or distortion. -
Q: What is the maximum supply voltage for TL07x op-amps?
A: The maximum supply voltage for TL07x op-amps is ±18 V. Exceeding this voltage can damage the op-amp and lead to improper operation or failure. -
Q: How can I reduce noise in TL07x op-amp circuits?
A: To reduce noise in TL07x op-amp circuits, consider the following techniques: - Use proper power supply decoupling capacitors close to the op-amp supply pins.
- Minimize the length of high-impedance traces to reduce the pickup of external noise.
- Use shielded cables for sensitive signals.
-
Implement appropriate filtering techniques, such as low-pass filters, to attenuate high-frequency noise.
-
Q: Can TL07x op-amps be used for high-frequency applications?
A: TL07x op-amps have a gain-bandwidth product of 3 MHz, which limits their use in high-frequency applications. For higher-frequency applications, consider using op-amps with a higher gain-bandwidth product, such as the TL08x series or other high-speed op-amps.
Conclusion
The TL07x series of operational amplifiers, including the TL071, TL072, and TL074, offer excellent performance characteristics and versatility for a wide range of analog circuit applications. With their low noise, high slew rate, and wide bandwidth, these op-amps are well-suited for tasks such as signal conditioning, filtering, and amplification.
By understanding the basic circuit configurations, such as inverting amplifiers, non-inverting amplifiers, and voltage followers, designers can effectively utilize TL07x op-amps in their projects. Advanced applications, such as active filters and instrumentation amplifiers, further demonstrate the capabilities of these op-amps.
When designing circuits with TL07x op-amps, it’s important to consider factors such as supply voltage range, noise reduction techniques, and frequency limitations. By following best practices and understanding the characteristics of these op-amps, designers can create robust and reliable analog circuits for various applications.
With their proven performance and widespread availability, the TL07x series of op-amps remains a popular choice among engineers and hobbyists alike. Whether you’re working on a simple amplifier circuit or a complex measurement system, the TL07x op-amps provide a solid foundation for your analog design needs.
No responses yet