Introduction to SMD Components and Polarity
Surface-mount devices (SMDs) have become increasingly popular in modern electronics due to their small size, high density, and efficient manufacturing processes. However, identifying the polarity of SMD components can be challenging, especially for beginners. In this article, we will discuss the polarity identification methods for common SMD components, including LEDs, capacitors, diodes, inductors, and integrated circuits (ICs).
What is Polarity in Electronic Components?
Polarity refers to the orientation or direction of current flow in an electronic component. In other words, it indicates which terminal is positive and which is negative. Proper polarity is crucial for the correct functioning of electronic circuits, as incorrect polarity can lead to component damage or circuit malfunction.
SMD LED Polarity Identification
SMD LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are widely used in various applications, such as indicators, displays, and lighting. Identifying the polarity of SMD LEDs is essential for proper operation and to avoid damage.
Visual Identification of SMD LED Polarity
Most SMD LEDs have visual indicators to help identify their polarity:
- Cathode Mark: The cathode (negative) terminal is usually indicated by a small dot, line, or chamfered edge on the LED package.
- Anode Pad: The anode (positive) pad is typically larger than the cathode pad.
Using a Multimeter to Determine SMD LED Polarity
If visual identification is not possible or unclear, a multimeter can be used to determine the polarity of an SMD LED:
- Set the multimeter to the diode test mode.
- Connect the red probe to one terminal and the black probe to the other.
- If the LED lights up, the red probe is connected to the anode, and the black probe is connected to the cathode.
- If the LED does not light up, reverse the probe connections and repeat the test.
SMD Capacitor Polarity Identification
SMD capacitors are essential components in various electronic circuits, used for filtering, coupling, and decoupling applications. While most SMD capacitors are non-polarized, some types, such as electrolytic and tantalum capacitors, have specific polarity requirements.
Non-Polarized SMD Capacitors
Most common SMD capacitors, such as ceramic, film, and mica capacitors, are non-polarized. They can be placed in either orientation on a PCB without affecting their functionality.
Polarized SMD Capacitors
Electrolytic and tantalum SMD capacitors are polarized and must be installed with the correct polarity to prevent damage and ensure proper operation.
- Electrolytic SMD Capacitors: The positive terminal is usually indicated by a “+” sign or a colored stripe on the capacitor body.
- Tantalum SMD Capacitors: The positive terminal is typically marked with a “+” sign or a colored dot on the capacitor body.

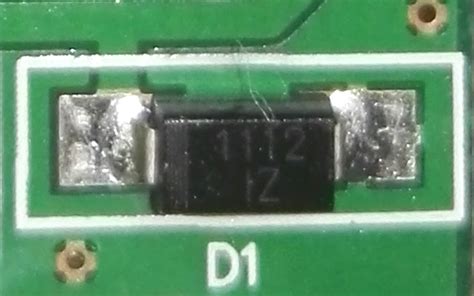
SMD Diode Polarity Identification
SMD diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction. Identifying the polarity of SMD diodes is crucial for proper circuit operation and to prevent damage.
Visual Identification of SMD Diode Polarity
Most SMD diodes have visual indicators to help identify their polarity:
- Cathode Mark: The cathode (negative) terminal is usually indicated by a stripe, band, or dot on the diode body.
- Anode Pad: In some cases, the anode (positive) pad may be larger than the cathode pad.
Using a Multimeter to Determine SMD Diode Polarity
A multimeter can be used to determine the polarity of an SMD diode:
- Set the multimeter to the diode test mode.
- Connect the red probe to one terminal and the black probe to the other.
- If the multimeter displays a forward voltage drop (usually 0.6-0.7V for silicon diodes), the red probe is connected to the anode, and the black probe is connected to the cathode.
- If the multimeter displays an open circuit or a high resistance, reverse the probe connections and repeat the test.
SMD Inductor Polarity Identification
SMD inductors are passive components that store energy in a magnetic field when current flows through them. Unlike some other SMD components, SMD inductors do not have a specific polarity requirement.
Non-Polarized SMD Inductors
Most SMD inductors are non-polarized and can be placed in either orientation on a PCB without affecting their functionality. However, it is essential to consider the inductor’s orientation with respect to nearby components to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure optimal performance.
SMD IC Polarity Identification
SMD integrated circuits (ICs) are complex components that contain multiple electronic circuits on a single chip. Identifying the polarity and pin assignments of SMD ICs is crucial for proper circuit operation and to prevent damage.
Visual Identification of SMD IC Polarity
SMD ICs have various package types, such as SOT, SOIC, QFP, and BGA. Each package has its own method for indicating pin assignments and polarity:
- Pin 1 Indicator: Most SMD ICs have a dot, notch, or chamfered edge near pin 1 to indicate the starting point for pin numbering.
- Pin Numbering: Pin numbers are usually printed on the IC package or can be found in the component’s datasheet.
Using Datasheets for SMD IC Polarity Identification
The most reliable method for identifying SMD IC polarity and pin assignments is to refer to the component’s datasheet. Datasheets provide detailed information about the IC’s package, pin assignments, and electrical characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can I use a multimeter to determine the polarity of all SMD components?
A: While a multimeter can be used to determine the polarity of SMD LEDs and diodes, it is not suitable for identifying the polarity of all SMD components. For example, polarized capacitors and ICs require visual identification or referring to their datasheets. -
Q: What happens if I install an SMD component with the wrong polarity?
A: Installing an SMD component with the wrong polarity can lead to component damage, circuit malfunction, or even complete failure of the device. It is essential to ensure correct polarity when assembling electronic circuits. -
Q: Are all SMD capacitors polarized?
A: No, not all SMD capacitors are polarized. Most common types, such as ceramic, film, and mica capacitors, are non-polarized and can be installed in either orientation. However, electrolytic and tantalum SMD capacitors are polarized and must be installed with the correct polarity. -
Q: How can I identify the polarity of an SMD component if there are no visual markings?
A: If there are no clear visual markings on an SMD component, refer to its datasheet for polarity and pin assignment information. Datasheets provide the most accurate and reliable information about a component’s characteristics and requirements. -
Q: Can I use the same polarity identification methods for through-hole components?
A: While some polarity identification methods, such as visual markings and multimeter testing, can be applied to through-hole components, the specific markings and pin assignments may differ. Always refer to the component’s datasheet for the most accurate information.
Conclusion
Identifying the polarity of SMD components is essential for proper circuit operation and to prevent damage. By understanding the various visual indicators, multimeter testing methods, and the importance of referring to datasheets, you can ensure correct polarity when working with SMD LEDs, capacitors, diodes, inductors, and ICs. Always take the time to double-check polarity before soldering components to a PCB, and consult datasheets when in doubt. With practice and attention to detail, identifying SMD polarity will become second nature, leading to more efficient and reliable electronic projects.
| Component | Polarity Identification Methods |
|---|---|
| SMD LED | – Visual: cathode mark, anode pad size – Multimeter: diode test mode |
| SMD Capacitor | – Non-polarized: ceramic, film, mica – Polarized: electrolytic (+ sign, stripe), tantalum (+ sign, dot) |
| SMD Diode | – Visual: cathode mark, anode pad size – Multimeter: diode test mode |
| SMD Inductor | – Non-polarized: can be placed in either orientation |
| SMD IC | – Visual: pin 1 indicator, pin numbering – Datasheet: package information, pin assignments |
By mastering SMD Polarity Identification, you’ll be well on your way to creating successful and reliable electronic projects. Remember to always prioritize safety, double-check your work, and refer to datasheets when in doubt. Happy soldering!
No responses yet