Understanding PCB Copper Thickness
What is PCB Copper Thickness?
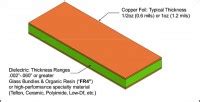
PCB copper thickness refers to the thickness of the copper layer deposited on the surface of the PCB substrate. The copper layer is responsible for carrying electrical signals and providing a conductive path for current flow. The thickness of the copper is typically measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²) or in microns (µm).
Copper Thickness Units
Copper thickness is commonly expressed in two different units:
- Ounces per Square Foot (oz/ft²):
- This is the standard unit used in the PCB industry.
- It represents the weight of copper deposited on a one-square-foot area of the PCB.
-
1 oz/ft² corresponds to a thickness of approximately 35 microns (µm) or 1.4 mils.
-
Microns (µm) or Micrometers:
- Micron is a metric unit of length equal to one-millionth of a meter.
- It is commonly used to express the thickness of the copper layer.
- 1 oz/ft² is equivalent to approximately 35 microns.
Standard Copper Thicknesses
PCBs can be manufactured with various copper thicknesses to suit different applications and requirements. Some standard copper thicknesses include:
| Copper Thickness (oz/ft²) | Copper Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|
| 0.5 oz | 17.5 µm |
| 1 oz | 35 µm |
| 2 oz | 70 µm |
| 3 oz | 105 µm |
| 4 oz | 140 µm |
The choice of copper thickness depends on factors such as current carrying capacity, power dissipation, and manufacturing constraints.
3 oz Copper Thickness
What is 3 oz Copper?
3 oz copper refers to a specific copper thickness used in PCB manufacturing. It means that the weight of copper deposited on a one-square-foot area of the PCB is 3 ounces. This corresponds to a thickness of approximately 105 microns (µm) or 4.2 mils.
Advantages of 3 oz Copper
Using 3 oz copper in PCB design offers several advantages:
- Increased Current Carrying Capacity:
- Thicker copper allows for higher current carrying capacity compared to thinner copper layers.
-
3 oz copper can handle higher currents without causing excessive heating or voltage drop.
-
Improved Thermal Management:
- Thicker copper helps in dissipating heat more efficiently.
-
It provides a larger cross-sectional area for heat conduction, reducing the risk of thermal issues.
-
Enhanced Mechanical Strength:
- 3 oz copper provides greater mechanical strength and stability to the PCB.
-
It reduces the likelihood of copper trace damage during handling and assembly.
-
Lower Resistance:
- Thicker copper results in lower electrical resistance.
- This minimizes voltage drop and improves overall electrical performance.
Applications of 3 oz Copper
3 oz copper is commonly used in PCB applications that require high current carrying capacity, efficient heat dissipation, and robustness. Some examples include:
- Power Electronics:
- PCBs for power supplies, motor drives, and inverters often utilize 3 oz copper.
-
The higher current handling capability ensures reliable operation under high power conditions.
-
Automotive Electronics:
- Automotive PCBs, especially those used in power distribution and control systems, benefit from 3 oz copper.
-
The increased copper thickness enhances the reliability and durability of the PCB in harsh automotive environments.
-
High-Current Connectors:
- PCBs with high-current connectors, such as those used in battery management systems or charging stations, may employ 3 oz copper.
-
The thicker copper ensures reliable and safe current transfer.
-
LED Lighting:
- LED lighting applications often require efficient heat dissipation to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
- 3 oz copper helps in effectively spreading and dissipating the heat generated by the LEDs.
PCB thickness Considerations
Factors Affecting PCB Thickness
The overall thickness of a PCB is influenced by several factors, including:
- Number of Layers:
- Multi-layer PCBs have multiple copper layers stacked and separated by insulating material.
-
The number of layers directly contributes to the overall thickness of the PCB.
-
Substrate Material:
- The choice of substrate material, such as FR-4, Rogers, or polyimide, affects the PCB thickness.
-
Different substrate materials have varying thicknesses and dielectric properties.
-
Copper Thickness:
- The thickness of the copper layer, such as 3 oz copper, adds to the overall PCB thickness.
-
Thicker copper layers result in a thicker PCB.
-
Solder Mask and Silkscreen:
- The application of solder mask and silkscreen layers slightly increases the PCB thickness.
- These layers provide insulation, protection, and labeling on the PCB surface.
PCB Thickness Calculation
To calculate the total thickness of a PCB, you need to consider the thicknesses of all the layers involved. Here’s a general formula:
Total PCB Thickness = Substrate Thickness + (Copper Thickness × Number of Copper Layers) + Solder Mask Thickness + Silkscreen Thickness
For example, let’s calculate the thickness of a 4-layer PCB with 3 oz copper:
- Substrate Thickness: 1.6 mm (standard FR-4)
- Copper Thickness: 0.105 mm (3 oz)
- Number of Copper Layers: 4
- Solder Mask Thickness: 0.025 mm (per side)
- Silkscreen Thickness: 0.015 mm (per side)
Total PCB Thickness = 1.6 mm + (0.105 mm × 4) + (0.025 mm × 2) + (0.015 mm × 2)
= 1.6 mm + 0.42 mm + 0.05 mm + 0.03 mm
= 2.1 mm (approximately)

FAQ
-
Q: What is the thickness of 3 oz copper in microns?
A: 3 oz copper has a thickness of approximately 105 microns (µm) or 4.2 mils. -
Q: How does the copper thickness affect the current carrying capacity of a PCB?
A: Thicker copper, such as 3 oz, allows for higher current carrying capacity compared to thinner copper layers. It can handle higher currents without causing excessive heating or voltage drop. -
Q: Is 3 oz copper suitable for high-power applications?
A: Yes, 3 oz copper is commonly used in high-power applications such as power electronics, automotive electronics, and high-current connectors. The increased copper thickness provides better current handling capability and thermal management. -
Q: How does the copper thickness impact the overall thickness of a PCB?
A: The copper thickness directly contributes to the overall thickness of a PCB. Thicker copper layers, like 3 oz, will result in a thicker PCB compared to thinner copper layers. -
Q: Can 3 oz copper be used in multi-layer PCBs?
A: Yes, 3 oz copper can be used in multi-layer PCBs. The number of layers and the thickness of each copper layer will determine the total thickness of the PCB.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of 3 oz copper thickness is crucial for PCB designers and manufacturers. With a thickness of approximately 105 microns, 3 oz copper offers several advantages, including increased current carrying capacity, improved thermal management, enhanced mechanical strength, and lower resistance. It finds applications in power electronics, automotive electronics, high-current connectors, and LED lighting.
When designing a PCB, it is essential to consider the copper thickness along with other factors such as the number of layers, substrate material, solder mask, and silkscreen. The overall PCB thickness can be calculated by summing up the thicknesses of all the layers involved.
By selecting the appropriate copper thickness, like 3 oz copper, designers can ensure that their PCBs meet the required electrical, thermal, and mechanical specifications. This ultimately leads to reliable and high-performance electronic devices.
No responses yet