
What is the use of Mcpcb?
Introduction to Metal-Core PCBs Metal-Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) are a specialized type of PCB that utilizes a metal base or substrate instead of the[…]

What is the alternative to FR4?
Introduction to PCB substrates In the world of printed circuit boards (PCBs), the choice of substrate material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and[…]
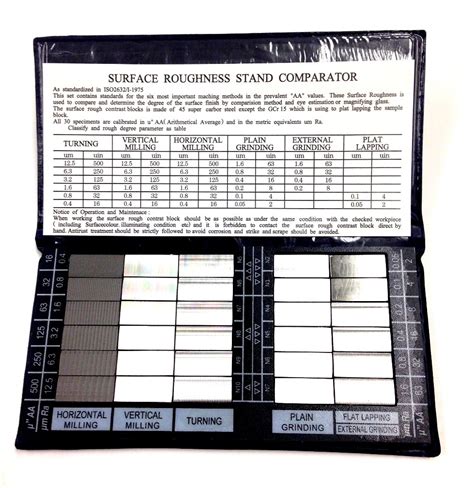
What is the surface roughness of RO4350B?
Understanding Surface Roughness Surface roughness is a measure of the irregularities and deviations on a material’s surface from its ideal, smooth form. These irregularities can[…]

What is RO4350B material?
Composition and Structure of RO4350B RO4350B is a composite material consisting of a reinforced hydrocarbon and ceramic laminate with low dielectric loss tangent and low[…]

What is Rogers 4000 material?
Key Features of Rogers 4000 Materials The Rogers 4000 series materials exhibit several key features that make them well-suited for high-frequency applications: Low dielectric constant[…]

What is PTFE PCB?
Characteristics of PTFE PCB Dielectric Properties PTFE boasts excellent dielectric properties, making it an ideal substrate for high-frequency applications. Its low dielectric constant (Dk) and[…]

What is the price range of a PCB?
Factors Affecting PCB Price Several factors contribute to the overall cost of a PCB. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions and optimize[…]

What is Rogers substrate?
Overview of Rogers substrate Rogers Corporation, founded in 1832, is a global leader in engineered materials solutions. The company has developed a range of advanced[…]
What is the point of PCB?
Introduction to PCBs and Their Purpose A printed circuit board, or PCB, is the backbone of nearly all modern electronic devices. PCBs are used to[…]

Why should we use PCB?
What is a PCB? A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a flat board made of insulating material, such as fiberglass or composite epoxy, with conductive[…]