
What is the thermal conductivity of a PCB board?
Understanding Thermal conductivity Thermal conductivity is a physical property that quantifies a material’s ability to conduct heat. It is defined as the rate at which[…]
What is the thermal conductivity of Rogers PCB material?
Introduction to Thermal Conductivity and Rogers PCB Thermal conductivity is a critical property of printed circuit board (PCB) materials, as it determines how effectively heat[…]
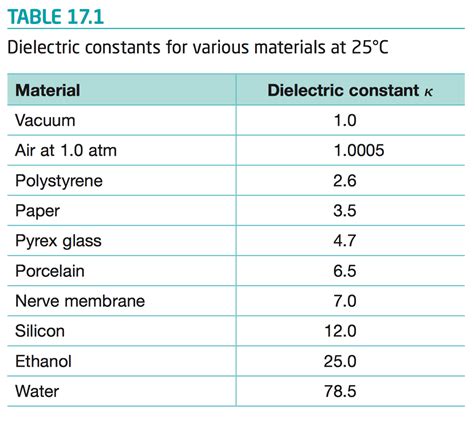
What is the dielectric constant of FR4 at 2.4 GHz?
Introduction to Dielectric constant and FR4 The dielectric constant, also known as the relative permittivity (εᵣ), is a fundamental property of an insulating material that[…]
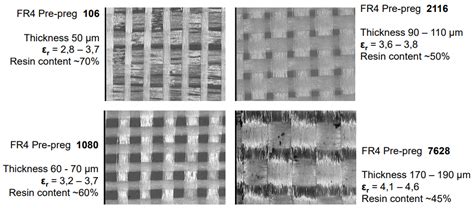
What is standard FR4?
Composition and Structure of FR4 FR4 is a composite material consisting of two main components: 1. Woven fiberglass cloth 2. Epoxy resin binder Woven Fiberglass[…]
What is the maximum length of a PCB?
Understanding PCB Length and Its Importance When designing and manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs), one crucial factor to consider is the PCB length. The length[…]

What is the standard PCB hole distance?
Understanding PCB hole distance PCB hole distance, also known as pitch, refers to the space between the centers of two adjacent holes on a printed[…]
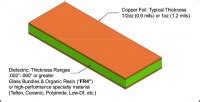
What is the range of PCB thickness?
Introduction to PCB thickness Printed Circuit Board (PCB) thickness is a crucial factor in the design and manufacturing of electronic devices. It plays a significant[…]
What is the frequency of a high speed PCB design?
Understanding PCB Frequency and High Speed Designs Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronic devices, enabling the interconnection and functionality of various[…]

How do you make high frequency PCB?
What is a High-frequency PCB? A high-frequency PCB is a printed circuit board designed to operate at frequencies above 100 MHz. These PCBs are characterized[…]
What is the highest frequency PCB?
What is a High-Frequency PCB? A high-frequency PCB is a specialized type of printed circuit board designed to operate at high frequencies, typically above 1[…]