How thin is the copper layer on a PCB?
Introduction to PCB Copper thickness Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They provide a platform for electrical components to be connected[…]
How thick is 3 oz copper on a PCB?
Understanding PCB Copper Thickness What is PCB Copper Thickness? PCB copper thickness refers to the thickness of the copper layer deposited on the surface of[…]

How thick is the copper on a PCB board?
Understanding PCB copper thickness PCB copper thickness refers to the thickness of the copper layer deposited on the surface of the PCB substrate material, typically[…]
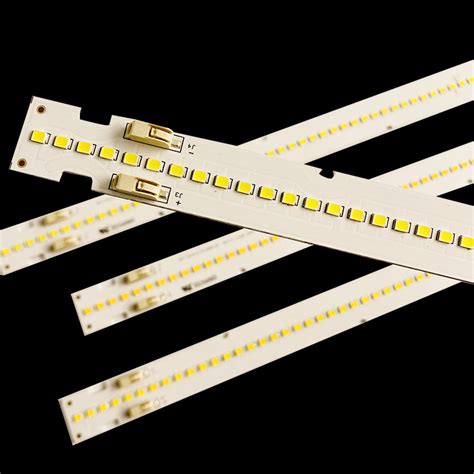

What is the difference between PCB and LED strip?
Introduction to PCB and LED strip Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and LED strips are two essential components in modern electronics. While they both play crucial[…]
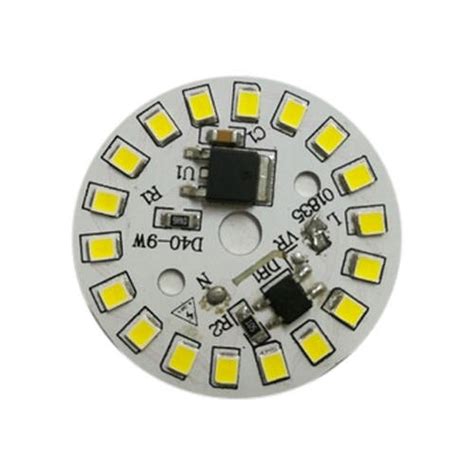

What does PCB LED mean?
Introduction to PCB LEDs PCB LED stands for Printed Circuit Board Light Emitting Diode. It is a type of LED that is mounted directly onto[…]
What is a PCB printed circuit board used for?
The Role of PCBs in Electronics The primary purpose of a PCB is to provide electrical connections between components in an electronic device. PCBs replace[…]
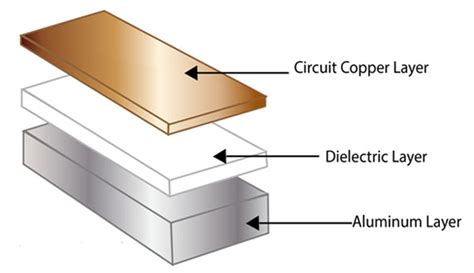
What are metal core PCBs used for?
Introduction to Metal-Core PCBs Metal-core PCBs, also known as MCPCBs or thermal management PCBs, are designed to address the challenges associated with heat generation and[…]
What is a ceramic PCB used for?
Introduction to Ceramic PCBs Ceramic printed circuit boards (PCBs) are a specialized type of PCB that utilizes ceramic materials as the substrate instead of the[…]
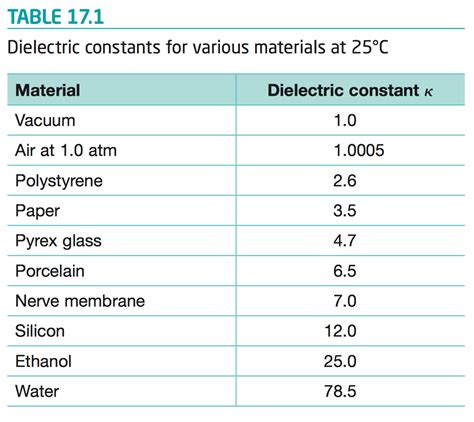
What is the dielectric constant of r04350b?
Understanding the dielectric constant The dielectric constant, also known as relative permittivity (εr), is a dimensionless quantity that describes the ability of a material to[…]
What is Rogers ro4350 material?
Key Properties of Rogers ro4350 Low Dielectric Constant and Loss Tangent One of the most critical characteristics of RO4350 is its low dielectric constant (Dk)[…]