What is the rating of FR4?
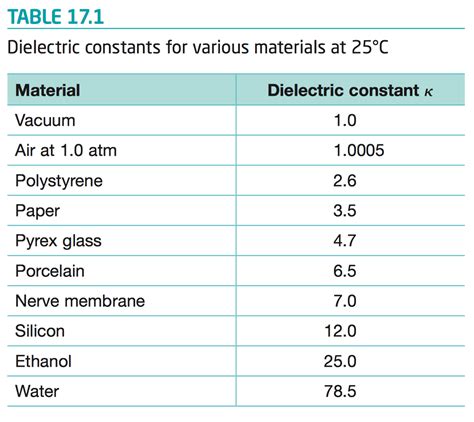
Understanding the Dielectric Constant The dielectric constant, also known as relative permittivity (εr), is a measure of a material’s ability to store electrical energy in[…]
What is the difference between a CEM and a 3D mammogram?
What is Contrast-Enhanced Mammography (CEM)? Contrast-enhanced mammography, also known as contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM), is an advanced x-ray imaging technique that combines a standard mammogram[…]

What is CEM in medical terms?
Key Components of CEM There are several key components that make up the CEM approach in medicine: 1. Comprehensive Patient Assessment The first step in[…]
What is CEM in radiology?
Introduction to Contrast-Enhanced Mammography Contrast-Enhanced Mammography (CEM) is an advanced imaging technique used in radiology to enhance the visualization and detection of breast abnormalities, particularly[…]
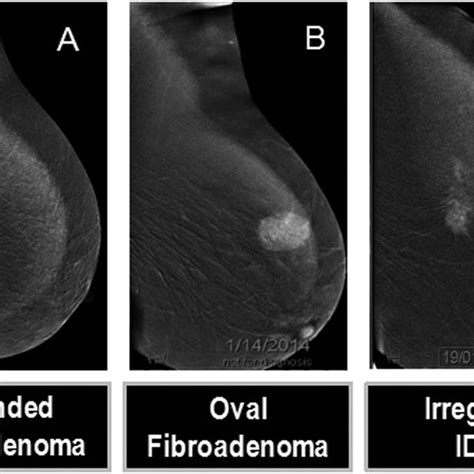
Why do I need a mammogram with contrast?
What is a Contrast mammogram? A contrast mammogram, also known as a contrast-enhanced mammogram or contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM), is a specialized type of mammogram[…]
What is FR1 PCB?
Characteristics of FR1 PCB Composition and Structure FR1 PCB is made from a composite material consisting of a paper base impregnated with a phenolic resin.[…]
What is the difference between FR1 and FR4?
Introduction to PCB Materials Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They provide a platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components, enabling[…]
What is CEM 1 material?
Composition and Structure of CEM1 Carbon Fiber Reinforcement The primary reinforcement in CEM1 is carbon fiber, which provides the material with its high strength-to-weight ratio[…]

What is the difference between CEM 1 and FR4?
Introduction to CEM-1 and FR-4 Materials CEM-1 (Composite Epoxy Material) and FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4) are two commonly used materials for manufacturing printed circuit boards[…]
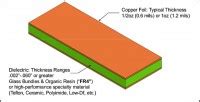
How thick is copper on FR4?
Understanding FR4 and its Properties {#understanding-fr4-and-its-properties} FR4 is a composite material made from woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin. The “FR” stands for[…]