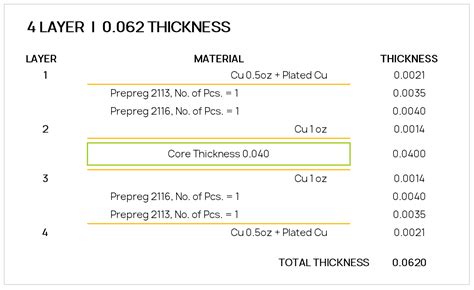
What is the standard PCB thickness?
Understanding PCB thickness PCB thickness is measured in either millimeters (mm) or mils (thousandths of an inch). The most common PCB thicknesses range from 0.4mm[…]

What is the frequency range of a high-speed PCB?
Factors Affecting High-Speed PCB Frequency Range Several factors come into play when determining the maximum frequency that a high-speed PCB can support. Let’s take a[…]
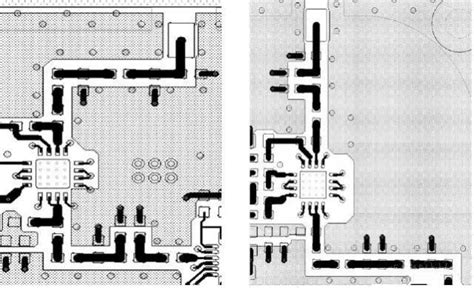
How to design a RF PCB?
Introduction to RF PCB Design Designing a radio frequency (RF) printed circuit board (PCB) requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and[…]

How do you make high current PCB?
Introduction to High-current PCB Design High-current printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential components in various electronic applications that require the efficient and reliable transmission of[…]
What materials are used in high frequency PCB?
Understanding High-frequency PCB materials What are High-Frequency PCBs? High-frequency PCBs are designed to operate at frequencies ranging from a few hundred megahertz (MHz) to several[…]
How to design high frequency PCB?
Understanding High Frequency PCB Design What is High Frequency PCB Design? High frequency PCB design refers to the design of printed circuit boards that operate[…]
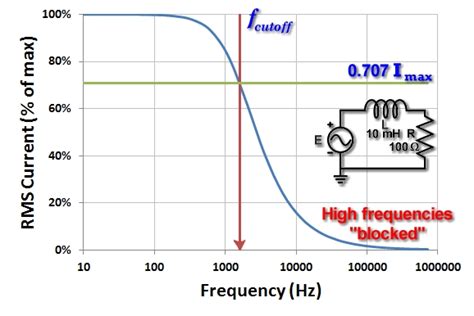
What is the maximum frequency of fr4?
Understanding FR4 Material Properties FR4 is a composite material made from woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. The “FR” stands for flame[…]
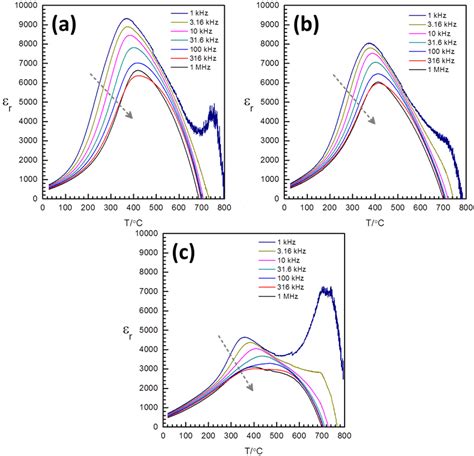
What is the permittivity of FR4?
Understanding Permittivity What is Permittivity? Permittivity is a measure of a material’s ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is a fundamental[…]
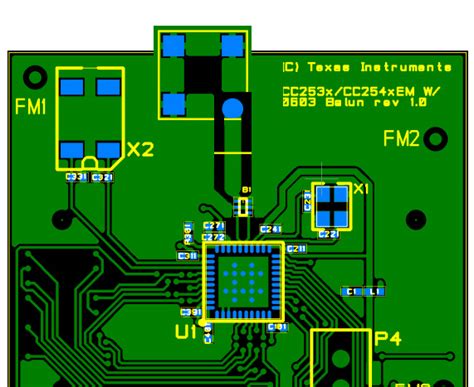
What are the traces for RF PCB?
Introduction to RF PCB Traces In the world of electronics, printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in connecting and supporting various components. When[…]
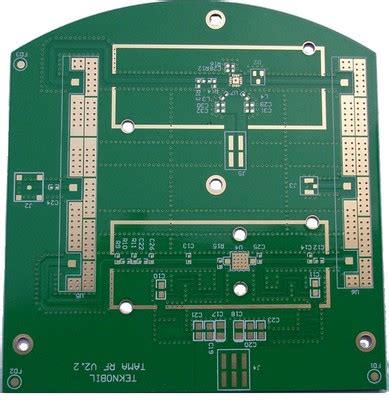
What is the difference between RF PCB and digital PCB?
Introduction to PCB Technology Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They provide a platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components, enabling[…]