Introduction to the Central Locking System
The central locking system is an essential feature in modern vehicles, providing convenience and security by allowing the driver to lock and unlock all the doors simultaneously using a remote key fob or a switch inside the car. The Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata, a popular sedan in the Chinese market, employs a sophisticated central locking system that ensures the safety and comfort of its occupants.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata’s central locking Circuit diagram, exploring its components, functionality, and common issues that may arise. By understanding the system’s inner workings, owners and technicians can better diagnose and resolve problems, ensuring the smooth operation of the central locking mechanism.
Components of the Central Locking System
The central locking system in the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata consists of several key components that work together to control the locking and unlocking of the doors. These components include:
- Central Locking Module (CLM)
- Door Lock Actuators
- Remote Key Fob
- Door Lock Switches
- Wiring Harness
Central Locking Module (CLM)
The Central Locking Module (CLM) is the brain of the central locking system. It is an electronic control unit (ECU) that receives signals from the remote key fob and door lock switches, processes the information, and sends commands to the door lock actuators to lock or unlock the doors accordingly.
The CLM is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of the vehicle. It is connected to the vehicle’s wiring harness and communicates with other electronic systems, such as the anti-theft system and the power window control module.
Door Lock Actuators
Door lock actuators are electromechanical devices that physically lock and unlock the doors when they receive signals from the CLM. Each door in the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata is equipped with its own actuator, which consists of a small electric motor and a gearbox that drives a locking mechanism.
When the CLM sends a locking or unlocking signal, the actuator motor rotates in the corresponding direction, engaging or disengaging the door lock. The actuators are designed to withstand the repeated use and vibrations encountered during the vehicle’s lifetime.
Remote Key Fob
The remote key fob is a handheld device that allows the driver to lock and unlock the doors remotely. It communicates with the CLM using radio frequency (RF) signals. When a button on the key fob is pressed, it sends a unique code to the CLM, which then verifies the code and initiates the appropriate action (locking or unlocking).
The remote key fob for the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata typically has buttons for locking, unlocking, and opening the trunk. Some models may also include additional features, such as a panic button or a remote engine start function.
Door Lock Switches
Door lock switches are manual controls that allow the occupants to lock and unlock the doors from inside the vehicle. In the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata, these switches are usually located on the door panels, within easy reach of the occupants.
When a door lock switch is pressed, it sends a signal to the CLM, which then commands the corresponding door lock actuator to lock or unlock the door. The driver’s door lock switch may also have a master control function that can lock or unlock all the doors simultaneously.
Wiring Harness
The wiring harness is a complex network of electrical wires and connectors that links the various components of the central locking system. It is responsible for transmitting power and signals between the CLM, door lock actuators, remote key fob receiver, and door lock switches.
The wiring harness is carefully designed to ensure reliable connections and minimize interference from other electrical systems in the vehicle. Each wire is color-coded and labeled to facilitate easy identification and troubleshooting.
Understanding the Circuit Diagram
The central locking circuit diagram is a visual representation of the electrical connections and components that make up the system. It uses standardized symbols and lines to depict the flow of power and signals between the various elements.
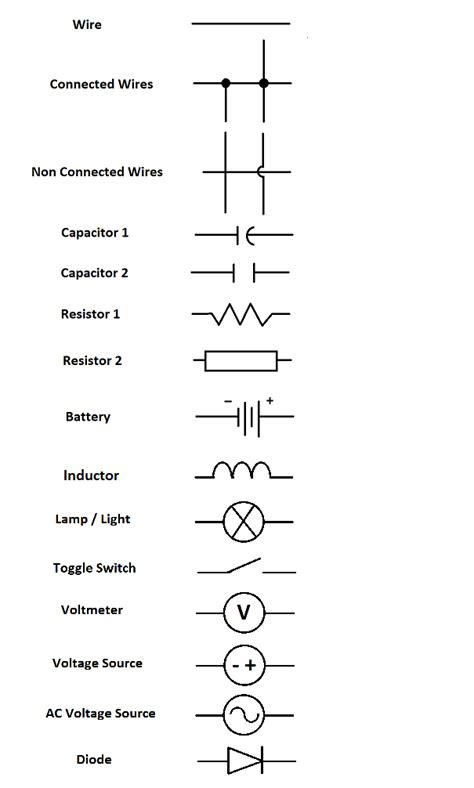
Circuit Diagram Symbols
To effectively read and interpret the central locking circuit diagram, it is essential to familiarize oneself with the common symbols used. Some of the key symbols include:
| Symbol | Component |
|---|---|
| Battery | |
| Fuse | |
| Ground | |
| Switch | |
| Motor | |
| Electronic Control Unit (ECU) |
Reading the Circuit Diagram
When examining the central locking circuit diagram for the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata, start by identifying the main components, such as the CLM, door lock actuators, remote key fob receiver, and door lock switches. Trace the power supply from the vehicle’s battery through the fuses and to the CLM.
Next, follow the signal paths between the CLM and the various input devices (remote key fob receiver and door lock switches) and output devices (door lock actuators). Pay attention to the color-coding of the wires and the pin numbers on the connectors to ensure accurate identification.
The circuit diagram will also include details on the specific voltages and current ratings required for each component, as well as any protective devices, such as diodes or relays, that are used to safeguard the system from voltage spikes or reverse polarity.

Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Like any electrical system, the central locking system in the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata may experience issues over time. Some of the most common problems include:
- Unresponsive remote key fob
- Door locks not working
- Intermittent locking or unlocking
- Central locking system failure
Unresponsive Remote Key Fob
If the remote key fob fails to lock or unlock the doors, the issue may lie with the key fob itself, the CLM, or the wiring harness. First, check the key fob battery and replace it if necessary. If the problem persists, inspect the remote key fob receiver and its connections for any signs of damage or loose wires.
If the key fob and receiver are functioning correctly, the issue may be with the CLM. Use the circuit diagram to test the input and output signals at the CLM connector, and replace the module if it is found to be faulty.
Door Locks Not Working
When one or more door locks fail to operate, the problem may be with the door lock actuator, the wiring harness, or the CLM. Begin by checking the actuator and its connections for any signs of damage or wear. Test the actuator using a multimeter to ensure it is receiving the correct voltage and ground signals.
If the actuator is functioning correctly, inspect the wiring harness for any frayed, broken, or short-circuited wires. Repair or replace any damaged sections as needed. If the wiring is intact, test the output signals from the CLM to the affected actuator and replace the CLM if it is not sending the proper commands.
Intermittent Locking or Unlocking
Intermittent locking or unlocking issues can be caused by a variety of factors, including loose connections, damaged wiring, or a faulty CLM. Start by inspecting all the connections in the central locking system, ensuring that they are clean, tight, and free from corrosion.
Next, check the wiring harness for any signs of damage or chafing, particularly in areas where the wires may be exposed to heat or movement. Repair or replace any damaged sections as needed.
If the connections and wiring are in good condition, the issue may lie with the CLM. Test the input and output signals at the CLM connector and replace the module if it is found to be faulty.
Central Locking System Failure
In rare cases, the entire central locking system may fail, leaving all the doors locked or unlocked. This issue is usually caused by a major fault in the CLM or a severe problem with the wiring harness.
Begin by checking the power supply to the CLM, ensuring that it is receiving the correct voltage and ground signals. If the power supply is intact, test the input and output signals at the CLM connector and replace the module if it is not functioning correctly.
If the CLM is working properly, inspect the entire wiring harness for any signs of damage or short circuits. Repair or replace any damaged sections as needed. In some cases, it may be necessary to replace the entire wiring harness if the damage is extensive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Can I replace the remote key fob battery myself?
Yes, replacing the remote key fob battery is a simple process that can be done at home. Refer to your owner’s manual for the specific steps and battery type required for your Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata. -
How do I know if my door lock actuator is failing?
Signs of a failing door lock actuator include a grinding or clicking noise when attempting to lock or unlock the door, a door that fails to lock or unlock consistently, or a door that remains locked or unlocked even when the central locking system is activated. -
Can I diagnose central locking system issues without a circuit diagram?
While it is possible to diagnose some central locking system issues without a circuit diagram, having access to the diagram can greatly simplify the troubleshooting process. The circuit diagram provides valuable information on the connections, voltages, and components involved, making it easier to pinpoint the source of the problem. -
Is it safe to repair the wiring harness myself?
Repairing the wiring harness can be a complex and delicate process, requiring a good understanding of electrical systems and proper tools. If you are not confident in your abilities, it is recommended to seek the help of a professional automotive electrician to avoid causing further damage to the system. -
How often should I have my central locking system inspected?
It is a good idea to have your central locking system inspected as part of your vehicle’s regular maintenance schedule, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles (whichever comes first). However, if you notice any issues with the system, such as inconsistent locking or unlocking, it is best to have it checked by a professional as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
Conclusion
The central locking system is a crucial component of the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata, providing both convenience and security for the vehicle’s occupants. By understanding the system’s components, circuit diagram, and common issues, owners and technicians can effectively diagnose and resolve problems, ensuring the smooth operation of the locking mechanism.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any issues can help prolong the life of the central locking system and prevent costly repairs in the future. If you are unsure about any aspect of the system or encounter a problem that you cannot resolve, do not hesitate to seek the assistance of a qualified automotive professional.
By familiarizing yourself with the Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata’s central locking circuit diagram and its intricacies, you can take a proactive approach to maintaining this essential feature of your vehicle, guaranteeing years of reliable and secure operation.
No responses yet