What is ENIG?
Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) is a surface finishing technology used in the production of printed Circuit boards (PCBs). It involves the deposition of a thin layer of nickel followed by a thin layer of gold on the copper pads of the PCB. The ENIG finish provides excellent solderability, good electrical conductivity, and superior corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for high-reliability applications.
The ENIG Process
The ENIG process consists of several steps:
- Cleaning: The PCB is thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants or oxide layers from the copper surface.
- Microetching: A mild etching solution is used to roughen the copper surface, improving the adhesion of the subsequent layers.
- Electroless Nickel Plating: The PCB is immersed in an electroless nickel plating solution, which deposits a thin layer of nickel (typically 3-6 μm) on the copper surface through an autocatalytic chemical reaction.
- Immersion Gold Plating: The nickel-plated PCB is then immersed in an immersion gold plating solution, which deposits a thin layer of gold (typically 0.05-0.2 μm) on top of the nickel layer through a displacement reaction.
- Rinsing and Drying: The PCB is rinsed with deionized water and dried to remove any residual chemicals.
Advantages of ENIG
ENIG offers several advantages over other surface finishes:
- Excellent Solderability: The gold layer provides excellent wettability and solderability, ensuring reliable solder joints.
- Flat Surface: ENIG produces a flat, planar surface, which is essential for fine-pitch components and high-density interconnects.
- Corrosion Resistance: The nickel layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying copper from corrosion and oxidation.
- Wire Bonding Compatibility: The gold surface is suitable for wire bonding, making ENIG a good choice for applications requiring wire bonding.
- Extended Shelf Life: ENIG-finished PCBs have a longer shelf life compared to other finishes, as the gold layer prevents oxidation of the underlying metals.
Disadvantages of ENIG
Despite its many advantages, ENIG also has some disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: ENIG is more expensive than other surface finishes due to the use of gold and the multi-step process involved.
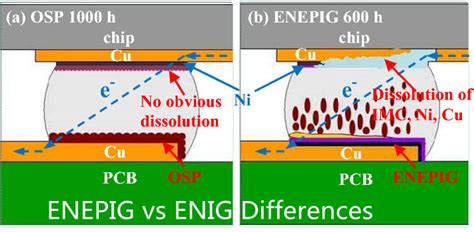
- Black Pad: In some cases, an intermetallic compound called “black pad” can form between the nickel and gold layers, leading to poor solderability and reduced reliability.
- Thin Gold Layer: The thin gold layer in ENIG may not be suitable for multiple reflow cycles or high-temperature applications.
ENIG vs. Other Surface Finishes
ENIG is one of several surface finishing options available for PCBs. Other common finishes include:
- Immersion Tin (ISn)
- Immersion Silver (IAg)
- Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP)
- Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL)
The table below compares the properties of these surface finishes:
| Property | ENIG | ISn | IAg | OSP | HASL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solderability | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++ |
| Flatness | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + |
| Corrosion Resistance | +++ | + | ++ | + | ++ |
| Wire Bonding | +++ | – | +++ | – | – |
| Shelf Life | +++ | + | ++ | + | ++ |
| Cost | +++ | + | ++ | + | ++ |
(+++ Excellent, ++ Good, + Fair, – Not Suitable)
Applications of ENIG
ENIG is widely used in various industries and applications that require high reliability and performance, such as:
- Automotive Electronics: ENIG’s excellent solderability and corrosion resistance make it suitable for automotive electronics exposed to harsh environments.
- Aerospace and Defense: The high reliability and long shelf life of ENIG-finished PCBs are essential for aerospace and defense applications.
- Medical Devices: ENIG’s biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion make it a good choice for medical devices and implantable electronics.
- High-Density Interconnects (HDI): The flat surface provided by ENIG is ideal for HDI PCBs with fine-pitch components and small geometries.
- Wire Bonding Applications: The gold surface of ENIG is compatible with wire bonding processes used in semiconductor packaging.

ENIG Quality Control and Testing
To ensure the quality and reliability of ENIG-finished PCBs, several tests and inspections are performed:
- Visual Inspection: The surface of the PCB is visually inspected for any defects, such as discoloration, blisters, or voids.
- Thickness Measurement: The thickness of the nickel and gold layers is measured using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or cross-sectional analysis to ensure they meet the specified requirements.
- Solderability Test: The solderability of the ENIG surface is assessed using the wetting balance test (IPC J-STD-003) or the dip and look test (IPC J-STD-002).
- Peel Strength Test: The adhesion between the ENIG layers and the underlying copper is evaluated using the peel strength test (IPC-TM-650 2.4.8).
- Porosity Test: The porosity of the nickel layer is assessed using the nitric acid test (IPC-TM-650 2.3.33) to ensure adequate coverage and protection of the underlying copper.
Selecting an ENIG Service Provider
When choosing an ENIG service provider, consider the following factors:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for a provider with a proven track record in ENIG processing and a deep understanding of the technology.
- Quality Control: Ensure that the provider has a robust quality control system in place, including regular testing and inspections.
- Certifications: Check if the provider holds relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or AS9100.
- Capacity and Lead Time: Verify that the provider has sufficient capacity to handle your production volume and can meet your required lead times.
- Technical Support: Choose a provider that offers excellent technical support and can assist you in troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the typical thickness of the nickel and gold layers in ENIG?
A: The typical thickness of the nickel layer is 3-6 μm, while the gold layer is usually 0.05-0.2 μm thick. -
Q: Can ENIG be used for high-temperature applications?
A: ENIG may not be suitable for high-temperature applications due to the thin gold layer, which can diffuse into the solder joint at elevated temperatures. -
Q: How does ENIG compare to HASL in terms of cost?
A: ENIG is generally more expensive than HASL due to the use of gold and the multi-step process involved. -
Q: What is the shelf life of ENIG-finished PCBs?
A: ENIG-finished PCBs have a longer shelf life compared to other finishes, typically 12 months or more when stored in a controlled environment. -
Q: Can ENIG be reworked or repaired?
A: Reworking or repairing ENIG-finished PCBs can be challenging due to the thin gold layer and the potential for damaging the underlying nickel and copper layers. Special care and techniques are required for successful rework or repair.
Conclusion
Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) is a popular surface finishing technology for Printed Circuit Boards, offering excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with fine-pitch components and wire bonding. While ENIG has some disadvantages, such as higher cost and the potential for black pad formation, its benefits make it a preferred choice for high-reliability applications in various industries.
When selecting an ENIG service provider, consider factors such as experience, quality control, certifications, capacity, and technical support to ensure the best results for your PCB projects. By understanding the ENIG process, its advantages and disadvantages, and the key considerations for choosing a provider, you can make informed decisions and achieve the desired performance and reliability for your electronic products.
No responses yet