Table of Contents
- BOM“>Introduction to Bill of Materials (BOM)
- Types of Bill of Materials
- Engineering Bill of Materials (EBOM)
- Manufacturing Bill of Materials (MBOM)
- Sales Bill of Materials (SBOM)
- Components of a Bill of Materials
- Part Number
- Part Name
- Description
- Quantity
- Unit of Measure (UOM)
- Procurement Type
- Reference Designators
- Importance of a Bill of Materials
- Procurement and Supply Chain Management
- Production Planning and Scheduling
- Inventory Management
- Quality Control
- Cost Estimation and Analysis
- Creating and Maintaining a Bill of Materials
- Gathering Information
- Structuring the BOM
- Reviewing and Approving the BOM
- Updating and Revising the BOM
- BOM Management Software
- Benefits of Using BOM Management Software
- Features to Look for in BOM Management Software
- Popular BOM Management Software Solutions
- Best Practices for BOM Management
- Standardize Part Numbering
- Maintain Accurate and Up-to-Date Information
- Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams
- Implement Version Control
- Conduct Regular Audits
- Challenges in BOM Management
- Managing Complex BOMs
- Dealing with Changes and Revisions
- Ensuring Data Integrity
- Integrating with Other Systems
- Future Trends in BOM Management
- Increased Adoption of Cloud-Based Solutions
- Integration with IoT and Smart Manufacturing
- Emphasis on Data Analytics and Insights
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Introduction to Bill of Materials (BOM)
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a structured list of all the components, parts, and materials required to produce a finished product. It provides a detailed breakdown of the product’s composition, including the quantity of each item needed, their respective part numbers, and any additional relevant information. The BOM serves as a critical reference document for various departments within an organization, such as engineering, procurement, production, and quality control.
The concept of a BOM has been around for centuries, with early examples dating back to the Industrial Revolution. However, the complexity and importance of BOMs have grown significantly in recent times, as products have become more intricate and supply chains have expanded globally. Today, effective BOM management is essential for companies to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and ensure the timely delivery of high-quality products.
Types of Bill of Materials
There are several types of BOMs, each serving a specific purpose and catering to the needs of different stakeholders within an organization. The three main types of BOMs are:
Engineering Bill of Materials (EBOM)
An Engineering Bill of Materials (EBOM) is created by the engineering team and focuses on the product’s design and functionality. It includes all the components and subassemblies necessary to create the product as designed, along with their specifications and technical details. The EBOM is typically used during the product development phase and serves as a blueprint for the manufacturing process.
Manufacturing Bill of Materials (MBOM)
A Manufacturing Bill of Materials (MBOM) is derived from the EBOM and is tailored to the specific requirements of the manufacturing process. It takes into account the production sequence, assembly instructions, and any additional materials or components needed for manufacturing. The MBOM may differ from the EBOM in terms of the order of components, the inclusion of packaging materials, or the substitution of equivalent parts based on availability or cost considerations.
Sales Bill of Materials (SBOM)
A Sales Bill of Materials (SBOM), also known as a Customer Bill of Materials (CBOM), is a simplified version of the BOM that focuses on the end product as sold to the customer. It includes only the top-level components or subassemblies that are relevant to the customer, without delving into the detailed breakdown of each component. The SBOM is often used by the sales and marketing teams to communicate the product’s features and configuration options to potential customers.
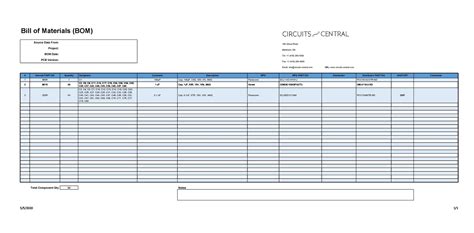
Components of a Bill of Materials
A typical BOM consists of several key components that provide essential information about each item included in the list. These components include:
Part Number
The part number is a unique identifier assigned to each component or subassembly in the BOM. It helps in tracking and referencing the item throughout the production process and in inventory management.
Part Name
The part name is a brief, descriptive title for each item in the BOM. It should clearly convey the nature or function of the component.
Description
The description provides additional details about the item, such as its specifications, materials, or any special characteristics. This information helps in ensuring that the correct component is used in the production process.
Quantity
The quantity indicates the number of units of a particular item required to produce one unit of the finished product. It is essential for accurate material planning and procurement.
Unit of Measure (UOM)
The unit of measure specifies the standard unit in which the quantity of the item is expressed, such as pieces, liters, or kilograms. Consistently using the appropriate UOM ensures clarity and accuracy in the BOM.
Procurement Type
The procurement type indicates whether the item is manufactured in-house, purchased from an external supplier, or a subcontracted component. This information is crucial for planning and managing the supply chain.
Reference Designators
Reference designators are alphanumeric codes that identify the specific location or plaCEMent of a component within the product’s design. They are particularly useful for complex products with numerous components, such as printed Circuit boards (PCBs).
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Part Number | Unique identifier for each component or subassembly |
| Part Name | Brief, descriptive title for each item |
| Description | Additional details about the item (specifications, materials, etc.) |
| Quantity | Number of units required to produce one unit of the finished product |
| Unit of Measure | Standard unit in which the quantity is expressed (pieces, liters, kg) |
| Procurement Type | Indicates if the item is manufactured in-house, purchased, or subcontracted |
| Reference Designators | Alphanumeric codes identifying the specific location of a component |
Importance of a Bill of Materials
A well-structured and maintained BOM is crucial for various aspects of the manufacturing process, including:
Procurement and Supply Chain Management
The BOM provides a clear list of all the components and materials required for production, enabling the procurement team to plan and manage the supply chain effectively. By identifying the required quantities and specifications of each item, the BOM helps in ensuring that the necessary components are ordered and delivered on time, avoiding production delays or stockouts.
Production Planning and Scheduling
The BOM serves as a foundation for production planning and scheduling. By understanding the components required and their respective quantities, production managers can optimize the manufacturing process, allocate resources efficiently, and create realistic production schedules. The BOM also helps in identifying potential bottlenecks or capacity constraints, allowing for proactive problem-solving.
Inventory Management
An accurate BOM is essential for effective inventory management. By knowing the exact quantities of components needed for each product, companies can maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking. The BOM also enables better tracking of inventory consumption, helping in forecasting future demand and planning for replenishment.
Quality Control
The BOM plays a vital role in ensuring product quality. By specifying the correct components and their respective specifications, the BOM helps in maintaining consistency and adherence to quality standards throughout the production process. Quality control teams can use the BOM as a reference to verify that the right components are being used and that the finished product meets the required specifications.
Cost Estimation and Analysis
The BOM is a valuable tool for cost estimation and analysis. By providing a detailed breakdown of the components and their quantities, the BOM enables accurate cost calculations for each product. This information is crucial for making informed pricing decisions, determining profit margins, and identifying opportunities for cost optimization. The BOM also allows for cost comparisons between different product variations or alternative components, facilitating cost-benefit analyses.
Creating and Maintaining a Bill of Materials
Creating and maintaining an accurate and up-to-date BOM is a collaborative effort involving multiple departments within an organization. The process typically involves the following steps:
Gathering Information
The first step in creating a BOM is to gather all the necessary information about the product’s components and subassemblies. This information can be obtained from various sources, such as engineering drawings, CAD models, supplier datasheets, and product specifications. It is essential to ensure that the information is accurate, complete, and up-to-date.
Structuring the BOM
Once the information is gathered, the next step is to structure the BOM in a hierarchical manner, reflecting the product’s assembly sequence and the relationships between components. The BOM should be organized in a logical and consistent format, making it easy to understand and navigate. Common BOM structures include single-level BOMs, multi-level BOMs, and modular BOMs, depending on the complexity of the product and the organization’s requirements.
Reviewing and Approving the BOM
After the BOM is structured, it should be reviewed and approved by the relevant stakeholders, such as engineering, production, and quality control teams. This review process ensures that the BOM is accurate, complete, and aligned with the product’s design and manufacturing requirements. Any discrepancies or issues identified during the review should be addressed and resolved before the BOM is finalized.
Updating and Revising the BOM
As products undergo changes and improvements, it is crucial to keep the BOM up-to-date. Any modifications to the product’s design, components, or specifications should be promptly reflected in the BOM. A well-defined change management process should be in place to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the changes and that the BOM is updated accordingly. Version control is essential to track the history of changes and maintain the integrity of the BOM.
BOM Management Software
Managing BOMs can be a complex and time-consuming task, especially for companies with extensive product portfolios or frequent product changes. To streamline the BOM management process, many organizations rely on specialized software solutions. BOM management software provides a centralized platform for creating, storing, and updating BOMs, making it easier to collaborate, track changes, and ensure data accuracy.
Benefits of Using BOM Management Software
-
Centralized Data Management: BOM management software provides a single, centralized repository for all BOM-related data, ensuring that everyone works with the most up-to-date and accurate information.
-
Improved Collaboration: With cloud-based BOM management solutions, teams can collaborate seamlessly, regardless of their location. Real-time updates and version control ensure that all stakeholders have access to the latest information.
-
Automated Processes: BOM management software can automate various tasks, such as generating part numbers, updating quantities, and tracking changes, reducing manual effort and minimizing the risk of errors.
-
Integration with Other Systems: Many BOM management solutions offer integration capabilities with other enterprise systems, such as ERP, MRP, and PLM, enabling seamless data exchange and ensuring consistency across the organization.
-
Enhanced Visibility and Traceability: BOM management software provides greater visibility into the product structure, component relationships, and change history, facilitating better decision-making and traceability.
Features to Look for in BOM Management Software
When selecting a BOM management software solution, consider the following key features:
-
User-Friendly Interface: The software should have an intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it easy for teams to create, view, and update BOMs.
-
Configurable BOM Structures: The software should support various BOM structures (single-level, multi-level, modular) to accommodate different product complexities and organizational needs.
-
Version Control and Change Management: Robust version control and change management capabilities are essential to track revisions, manage changes, and maintain a complete history of the BOM.
-
Access Control and Security: The software should provide granular access control and security features to ensure that only authorized users can view or modify the BOM data.
-
Integration Capabilities: Look for software that can integrate with your existing enterprise systems, such as ERP, MRP, and PLM, to ensure seamless data flow and avoid duplication of effort.
-
Reporting and Analytics: The software should offer robust reporting and analytics features, enabling users to generate custom reports, track key metrics, and gain insights into BOM-related data.
Popular BOM Management Software Solutions
Some popular BOM management software solutions include:
- Autodesk PLM 360
- OpenBOM
- Arena BOM
- Omnify Software
- Deskera ERP
Best Practices for BOM Management
To ensure effective BOM management, consider the following best practices:
Standardize Part Numbering
Establish a consistent and standardized part numbering system to uniquely identify each component and subassembly in the BOM. This helps in avoiding confusion and ensuring that the right parts are used in the production process.
Maintain Accurate and Up-to-Date Information
Regularly review and update the BOM to ensure that it reflects the latest product design and specifications. Encourage cross-functional collaboration to identify and address any discrepancies or changes in a timely manner.
Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams
Foster collaboration among engineering, procurement, production, and quality control teams to ensure that the BOM meets the requirements of all stakeholders. Regular communication and feedback loops can help in identifying potential issues and opportunities for improvement.
Implement Version Control
Establish a robust version control system to track changes and revisions to the BOM. This ensures that everyone works with the most up-to-date information and maintains a complete history of the BOM’s evolution.
Conduct Regular Audits
Perform periodic audits of the BOM to verify its accuracy and completeness. This helps in identifying any discrepancies, obsolete components, or potential areas for optimization.
Challenges in BOM Management
Despite the benefits of effective BOM management, organizations may face several challenges, including:
Managing Complex BOMs
As products become more complex and involve a greater number of components and subassemblies, managing BOMs can become increasingly challenging. Ensuring data accuracy, maintaining relationships between components, and handling multiple BOM levels can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Dealing with Changes and Revisions
Frequent changes to product designs, components, or specifications can make it difficult to keep the BOM up-to-date. Managing revisions, ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of the changes, and maintaining a complete change history can be complex and resource-intensive.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Maintaining the accuracy and integrity of BOM data across multiple systems and departments can be a challenge. Inconsistencies, duplication of data, or lack of synchronization between systems can lead to errors and inefficiencies in the production process.
Integrating with Other Systems
Integrating BOM management with other enterprise systems, such as ERP, MRP, and PLM, can be complex and require significant effort. Ensuring seamless data exchange, avoiding duplication of data, and maintaining consistency across systems can be challenging.
Future Trends in BOM Management
As technology advances and manufacturing processes evolve, BOM management is expected to undergo significant changes. Some of the future trends in BOM management include:
No responses yet