Introduction to PCB Stencils and Openings
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) stencils are essential tools in the electronics manufacturing process. They are used to apply solder paste onto the PCB pads, ensuring precise and consistent solder paste deposition. One of the critical aspects of PCB stencil design is creating openings that allow the solder paste to be deposited accurately on the pads. In this article, we will discuss the five best tips for creating openings on PCB stencils to achieve optimal results.
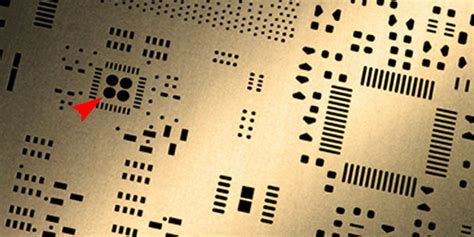
What are PCB Stencil Openings?
PCB stencil openings, also known as apertures, are the holes or cut-outs in the stencil that allow the solder paste to pass through and be deposited onto the PCB pads. The openings are typically designed to match the size and shape of the pads on the PCB. Properly designed openings ensure that the right amount of solder paste is applied to each pad, resulting in reliable solder joints and improved production yields.
Tip 1: Determine the Appropriate Opening Size
The first tip for creating openings on PCB stencils is to determine the appropriate opening size. The opening size should be based on the size of the PCB pads and the type of components being used. Generally, the opening size should be slightly larger than the pad size to allow for proper solder paste release.
Factors Affecting Opening Size
Several factors can affect the optimal opening size for PCB stencils:
-
Pad Size: The opening size should be based on the size of the PCB pads. As a general rule, the opening should be 1-2 mils (0.025-0.05 mm) larger than the pad size on all sides.
-
Component Type: The type of components being used can also influence the opening size. For example, fine-pitch components may require smaller openings to prevent solder bridging, while larger components may need larger openings to ensure sufficient solder paste deposition.
-
Solder Paste Type: The properties of the solder paste, such as viscosity and particle size, can affect the optimal opening size. Higher viscosity solder pastes may require larger openings for proper release, while smaller particle sizes may allow for smaller openings.
Opening Size Guidelines
Here are some general guidelines for determining the appropriate opening size based on the pad size:
| Pad Size (mils) | Opening Size (mils) |
|---|---|
| 10-20 | Pad Size + 2-4 |
| 20-30 | Pad Size + 3-5 |
| 30-50 | Pad Size + 4-6 |
| 50-100 | Pad Size + 5-7 |
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual opening size may need to be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the PCB design and manufacturing process.
Tip 2: Consider the Stencil Thickness
The second tip for creating openings on PCB stencils is to consider the stencil thickness. The stencil thickness plays a crucial role in determining the volume of solder paste deposited on the pads. Thicker stencils deposit more solder paste, while thinner stencils deposit less.
Choosing the Right Stencil Thickness
The optimal stencil thickness depends on several factors, including the size of the PCB pads, the component pitch, and the desired solder paste volume. Here are some general guidelines for choosing the appropriate stencil thickness:
| Pad Size (mils) | Stencil Thickness (mils) |
|---|---|
| < 10 | 4-5 |
| 10-20 | 5-6 |
| 20-30 | 6-8 |
| 30-50 | 8-10 |
| > 50 | 10-12 |
It’s important to consider the aspect ratio when selecting the stencil thickness. The aspect ratio is the ratio of the aperture width to the stencil thickness. A higher aspect ratio (larger aperture width relative to the stencil thickness) allows for better solder paste release, while a lower aspect ratio may result in insufficient paste deposition.
Stencil Thickness and Opening Size
The stencil thickness also affects the opening size. As the stencil thickness increases, the opening size may need to be adjusted to maintain the desired aspect ratio and ensure proper solder paste release. Thicker stencils may require larger openings to compensate for the increased thickness.

Tip 3: Optimize the Opening Shape
The third tip for creating openings on PCB stencils is to optimize the opening shape. The shape of the opening can significantly affect the solder paste deposition and the resulting solder joint quality.
Common Opening Shapes
There are several common opening shapes used in PCB stencils:
-
Rectangle: Rectangular openings are the most common and are suitable for most pad shapes. They provide good solder paste coverage and are easy to manufacture.
-
Circle: Circular openings are used for round pads, such as those found on Ball Grid Array (BGA) components. They ensure even solder paste distribution around the pad.
-
Oblong: Oblong openings, also known as oval openings, are used for elongated pads or pads with limited space. They provide better paste coverage than rectangular openings in these situations.
-
D-Shape: D-shaped openings are a combination of rectangular and circular shapes. They are used for pads with one rounded end, such as those found on some connectors.
Optimizing the Opening Shape
When optimizing the opening shape, consider the following factors:
-
Pad Shape: The opening shape should match the shape of the pad as closely as possible to ensure proper solder paste coverage.
-
Aspect Ratio: The aspect ratio of the opening should be appropriate for the stencil thickness to ensure good solder paste release. A higher aspect ratio is generally preferred.
-
Solder Paste Flow: The opening shape should allow for smooth solder paste flow and prevent clogging. Avoid sharp corners or narrow sections that may hinder paste release.
-
Manufacturing Limitations: Consider the limitations of the stencil manufacturing process when selecting the opening shape. Some complex shapes may be difficult or expensive to manufacture.
Tip 4: Incorporate Stencil Escape Openings
The fourth tip for creating openings on PCB stencils is to incorporate stencil escape openings. Escape openings, also known as relief openings or dump openings, are additional openings placed adjacent to the main openings to provide a path for excess solder paste to escape.
Benefits of Stencil Escape Openings
Stencil escape openings offer several benefits:
-
Reduced Solder Bridging: Escape openings help prevent solder bridging between adjacent pads by providing a path for excess solder paste to flow away from the main openings.
-
Improved Solder Paste Release: Escape openings improve solder paste release by reducing the pressure buildup during the printing process. This results in better paste deposition and fewer defects.
-
Enhanced Printing Consistency: By allowing excess solder paste to escape, stencil escape openings contribute to more consistent solder paste deposition across the PCB.
Designing Stencil Escape Openings
When designing stencil escape openings, consider the following guidelines:
-
Size: The escape opening should be smaller than the main opening to prevent excessive solder paste loss. A typical escape opening size is 50-70% of the main opening size.
-
Location: Place the escape openings adjacent to the main openings, typically on the outer edges. Avoid placing them too close to neighboring pads to prevent solder bridging.
-
Shape: Escape openings can be rectangular, circular, or triangular in shape. The shape should be chosen based on the available space and the pad layout.
-
Number: The number of escape openings depends on the size and shape of the main opening. Larger or more complex openings may require multiple escape openings for effective solder paste release.
Tip 5: Perform Stencil Design Verification
The fifth tip for creating openings on PCB stencils is to perform stencil design verification. Before manufacturing the stencil, it’s crucial to verify the design to ensure that the openings are correctly sized, shaped, and positioned.
Stencil Design Verification Methods
There are several methods for verifying the stencil design:
-
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Review: Use CAD software to review the stencil design and check for any errors or discrepancies. Compare the stencil design with the PCB layout to ensure that the openings align with the pads.
-
Gerber File Comparison: Compare the stencil Gerber files with the PCB Gerber files to verify that the openings match the pad sizes and locations. Use Gerber viewer software to overlay the stencil and PCB files and check for any misalignments.
-
Design Rule Check (DRC): Perform a DRC on the stencil design to identify any design rule violations, such as minimum opening size, spacing, or aspect ratio. Use stencil-specific DRC rules to ensure that the design meets the manufacturing requirements.
-
Stencil Simulation: Use stencil simulation software to visualize the solder paste deposition process and identify any potential issues, such as insufficient paste coverage or solder bridging. Simulate different stencil thicknesses and opening sizes to optimize the design.
Benefits of Stencil Design Verification
Performing stencil design verification offers several benefits:
-
Error Detection: Verification helps identify and correct design errors before manufacturing the stencil, reducing the risk of defects and rework.
-
Optimization Opportunities: By analyzing the stencil design, you can identify opportunities for optimization, such as adjusting opening sizes or shapes to improve solder paste deposition.
-
Cost Savings: Catching and correcting design issues early in the process can save time and money by avoiding the need for stencil rework or replacement.
-
Improved Quality: A verified stencil design contributes to higher-quality solder paste deposition, resulting in better solder joint reliability and overall PCB quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the recommended opening size for a 25-mil pad?
A: For a 25-mil pad, the recommended opening size is typically 28-30 mils (pad size + 3-5 mils). -
Q: How does stencil thickness affect solder paste deposition?
A: Thicker stencils deposit more solder paste, while thinner stencils deposit less. The optimal stencil thickness depends on factors such as pad size, component pitch, and desired solder paste volume. -
Q: What are the most common opening shapes used in PCB stencils?
A: The most common opening shapes are rectangles, circles, oblongs (ovals), and D-shapes. The choice of shape depends on the pad shape and the specific requirements of the PCB design. -
Q: What are stencil escape openings, and why are they used?
A: Stencil escape openings, also known as relief openings or dump openings, are additional openings placed adjacent to the main openings to provide a path for excess solder paste to escape. They help reduce solder bridging, improve solder paste release, and enhance printing consistency. -
Q: Why is stencil design verification important?
A: Stencil design verification is important to ensure that the openings are correctly sized, shaped, and positioned before manufacturing the stencil. It helps identify and correct design errors, optimize the design, save costs, and improve the overall quality of the solder paste deposition process.
Conclusion
Creating openings on PCB stencils is a critical aspect of ensuring accurate and reliable solder paste deposition. By following the five tips discussed in this article – determining the appropriate opening size, considering the stencil thickness, optimizing the opening shape, incorporating stencil escape openings, and performing stencil design verification – you can create high-quality stencils that contribute to better PCB manufacturing results.
Remember to consider the specific requirements of your PCB design, such as pad sizes, component types, and manufacturing limitations, when creating stencil openings. Regularly review and optimize your stencil designs to continuously improve the solder paste deposition process and achieve the best possible outcomes for your PCB assembly projects.
No responses yet