Are PCB boards durable?
What Makes a PCB Durable? PCB durability is determined by several factors, including: Materials used Manufacturing process Environmental factors Design considerations Materials Used in PCB[…]
What is the dielectric strength of FR4 in kV MM?
Understanding Dielectric strength Dielectric strength, also known as breakdown voltage, is the maximum electric field strength that an insulating material can withstand before it experiences[…]
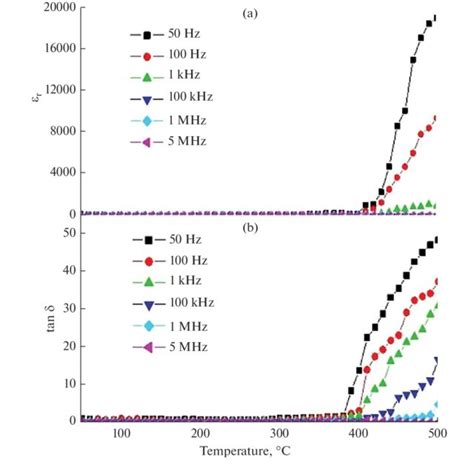
What is the dissipation factor of FR4?
Introduction to Dissipation Factor Dissipation factor, also known as loss tangent or tan δ, is a critical parameter in the characterization of dielectric materials, such[…]
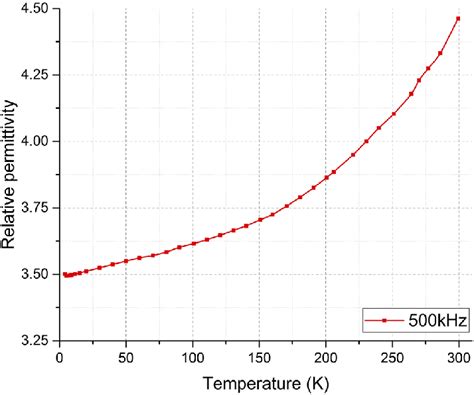
What is the strength of FR4 material?
Understanding FR4 Material FR4 is a composite material made from woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. The “FR” in FR4 stands for[…]
Why we use FR4 substrate?
What is FR4 substrate? FR4 substrate, also known as FR-4 laminate, is a widely used material in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It[…]

What is Cem used for?
Types of Cement Before diving into the uses of cement, it’s important to understand the different types available. The most common types of cement include:[…]

What is the difference between CEM-1 and FR 1?
Overview of CEM-1 vs FR-1 CEM-1 (Composite Epoxy Material) and FR-1 (Flame Retardant) are two types of materials used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). Both[…]

How thick is the copper in Mcpcb?
Understanding McPCB copper thickness Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) are specialized PCBs that use a metal substrate, typically aluminum, instead of the traditional FR-4[…]

What is Mcpcb LED?
Introduction to LED-MCPCB LED-MCPCB, or Metal Core Printed Circuit Board LED, is a revolutionary technology that combines the efficiency and durability of LEDs with the[…]

What is the use of Mcpcb?
Introduction to Metal-Core PCBs Metal-Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) are a specialized type of PCB that utilizes a metal base or substrate instead of the[…]