What is the application of PCB?
Introduction to PCB and its Applications Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They are used in almost every electronic device we[…]
What are the raw materials used in PCB?
Types of PCB Materials There are several types of materials used in PCB manufacturing, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. The most common[…]

What type of plastic is PCB made from?
PCB Substrate Materials The substrate, or base material, of a PCB is typically made from a non-conductive and heat-resistant material. The most common substrate materials[…]

What is the composition of a PCB?
PCB Substrate Materials The substrate, or base material, of a PCB provides the foundation upon which the copper traces and other components are placed. The[…]
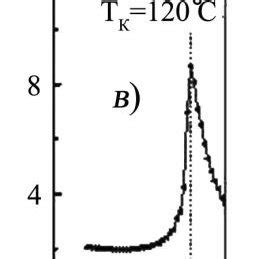
What is the dielectric permeability of FR4?
Understanding Dielectric permeability Dielectric permeability, also known as relative permittivity, is a measure of a material’s ability to store electrical energy in an electric field.[…]
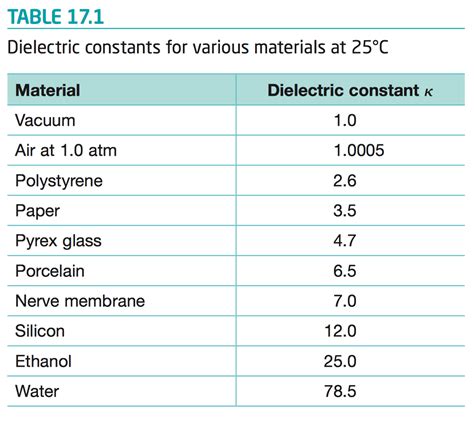
What is the dielectric constant of FR4 PCB?
Understanding the Dielectric constant The dielectric constant, also known as relative permittivity (εr), is a measure of a material’s ability to store electrical energy in[…]
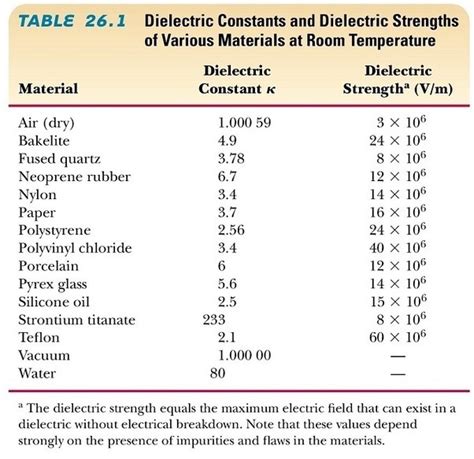
What is the dielectric strength of FR4?
What is Dielectric Strength? Dielectric strength, also known as the breakdown voltage, is a measure of a material’s ability to resist electrical breakdown under an[…]
What is the resistivity of FR4?
Understanding FR4 Material FR4 is a composite material consisting of a woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. The fiberglass reinforcement provides mechanical[…]
Is FR4 a thermal insulator?
What is Thermal Insulation? Thermal insulation is the process of reducing heat transfer between objects or environments with different temperatures. Materials that have low thermal[…]
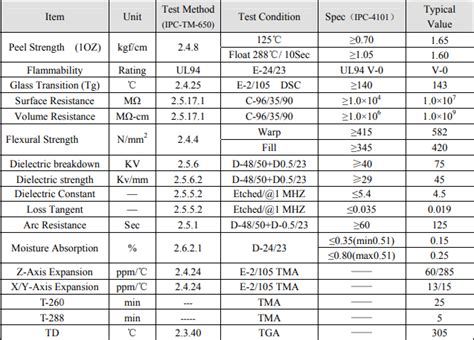
What is the temperature rating for FR4?
Introduction to FR4 and Its Temperature Characteristics FR4, or Flame Retardant 4, is a widely used material in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs).[…]