Understanding PCB Thickness
When designing and manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs), one of the essential factors to consider is the thickness of the board. The thickness of a PCB can affect its mechanical strength, electrical properties, and overall functionality. In this article, we will focus on the thickness of a 2 layer PCB and explore the factors that influence its dimensions.
What is a 2 Layer PCB?
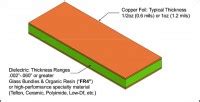
A 2 layer PCB, also known as a double-sided PCB, is a printed circuit board that consists of two conductive copper layers separated by an insulating substrate. The copper layers are used to route electrical signals and provide a foundation for mounting electronic components. The insulating substrate, typically made of materials such as FR-4 or Rogers, provides mechanical support and electrical isolation between the layers.
Factors Affecting PCB Thickness
Several factors contribute to the overall thickness of a 2 layer PCB:
-
Copper Weight: The thickness of the copper layers is measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²). Common copper weights for 2 layer PCBs include 0.5 oz, 1 oz, and 2 oz. The higher the copper weight, the thicker the copper layer.
-
Substrate Thickness: The thickness of the insulating substrate plays a significant role in determining the overall PCB thickness. Standard substrate thicknesses for 2 layer PCBs range from 0.2 mm to 1.6 mm.
-
Solder Mask and Silkscreen: The application of solder mask and silkscreen layers on the PCB surface adds to the overall thickness. These layers are typically thin, ranging from 0.01 mm to 0.03 mm.
-
Manufacturing Tolerances: PCB manufacturers have specific tolerances for the thickness of each layer and the overall board. These tolerances can vary depending on the manufacturing process and the specified requirements.
Standard 2 Layer PCB Thicknesses
The following table presents the standard thicknesses for 2 layer PCBs based on the combination of copper weight and substrate thickness:
| Copper Weight | Substrate Thickness | Overall PCB Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 oz | 0.2 mm | 0.4 mm |
| 0.5 oz | 0.4 mm | 0.6 mm |
| 0.5 oz | 0.8 mm | 1.0 mm |
| 1 oz | 0.2 mm | 0.6 mm |
| 1 oz | 0.4 mm | 0.8 mm |
| 1 oz | 0.8 mm | 1.2 mm |
| 2 oz | 0.4 mm | 1.0 mm |
| 2 oz | 0.8 mm | 1.4 mm |
| 2 oz | 1.6 mm | 2.2 mm |
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual thickness of a 2 layer PCB may vary slightly based on the specific manufacturing process and tolerances.
Choosing the Right PCB Thickness
When selecting the appropriate thickness for your 2 layer PCB, consider the following factors:
-
Mechanical Requirements: The PCB thickness should provide sufficient mechanical strength to withstand the expected stress and strain during assembly, handling, and operation. Thicker PCBs offer better rigidity and durability.
-
Electrical Requirements: The thickness of the copper layers and the substrate can impact the electrical properties of the PCB, such as impedance, signal integrity, and power handling capability. Choose a thickness that meets your electrical design requirements.
-
Component Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen PCB thickness is compatible with the components and connectors that will be mounted on the board. Some components may have specific height restrictions or require a certain PCB thickness for proper mounting and soldering.
-
Manufacturing Constraints: Consider the capabilities and limitations of your PCB manufacturer. Some manufacturers may have minimum or maximum thickness limitations based on their equipment and processes. Discuss your thickness requirements with your manufacturer to ensure feasibility and optimal results.

FAQ
-
Q: Can I customize the thickness of my 2 layer PCB?
A: Yes, you can work with your PCB manufacturer to customize the thickness of your 2 layer PCB based on your specific requirements. However, keep in mind that custom thicknesses may incur additional costs and longer lead times compared to standard thicknesses. -
Q: How does the thickness of a 2 layer PCB affect its cost?
A: Generally, thicker 2 layer PCBs tend to be more expensive than thinner ones. This is because thicker boards require more material (copper and substrate) and may involve additional manufacturing steps. However, the cost difference may not be significant for low-volume production or prototype runs. -
Q: What is the minimum thickness for a 2 layer PCB?
A: The minimum thickness for a 2 layer PCB is typically around 0.4 mm, which corresponds to a combination of 0.5 oz copper weight and a 0.2 mm substrate. However, the actual minimum thickness may vary depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities and the specific design requirements. -
Q: Can I mix different copper weights on a 2 layer PCB?
A: Yes, it is possible to have different copper weights on the top and bottom layers of a 2 layer PCB. This is known as a “mixed copper” design. Mixed copper designs can be useful for optimizing electrical performance or meeting specific requirements for power and signal routing. -
Q: How does the PCB thickness affect the assembly process?
A: The thickness of a 2 layer PCB can impact the assembly process in several ways. Thicker boards may require longer soldering times and higher soldering temperatures to ensure proper component attachment. Additionally, thicker boards may be more challenging to route through automated assembly equipment, especially for fine-pitch components.
Conclusion
Understanding the thickness of a 2 layer PCB is crucial for designing and manufacturing reliable and functional electronic devices. The thickness of a 2 layer PCB is determined by factors such as copper weight, substrate thickness, solder mask, silkscreen, and manufacturing tolerances. Standard thicknesses for 2 layer PCBs range from 0.4 mm to 2.2 mm, depending on the combination of copper weight and substrate thickness.
When choosing the appropriate thickness for your 2 layer PCB, consider the mechanical requirements, electrical requirements, component compatibility, and manufacturing constraints. Work closely with your PCB manufacturer to ensure that your thickness requirements are feasible and optimized for your specific application.
By selecting the right PCB thickness, you can ensure the optimal performance, reliability, and manufacturability of your electronic devices.
No responses yet